The Basics of Define Freight on Board
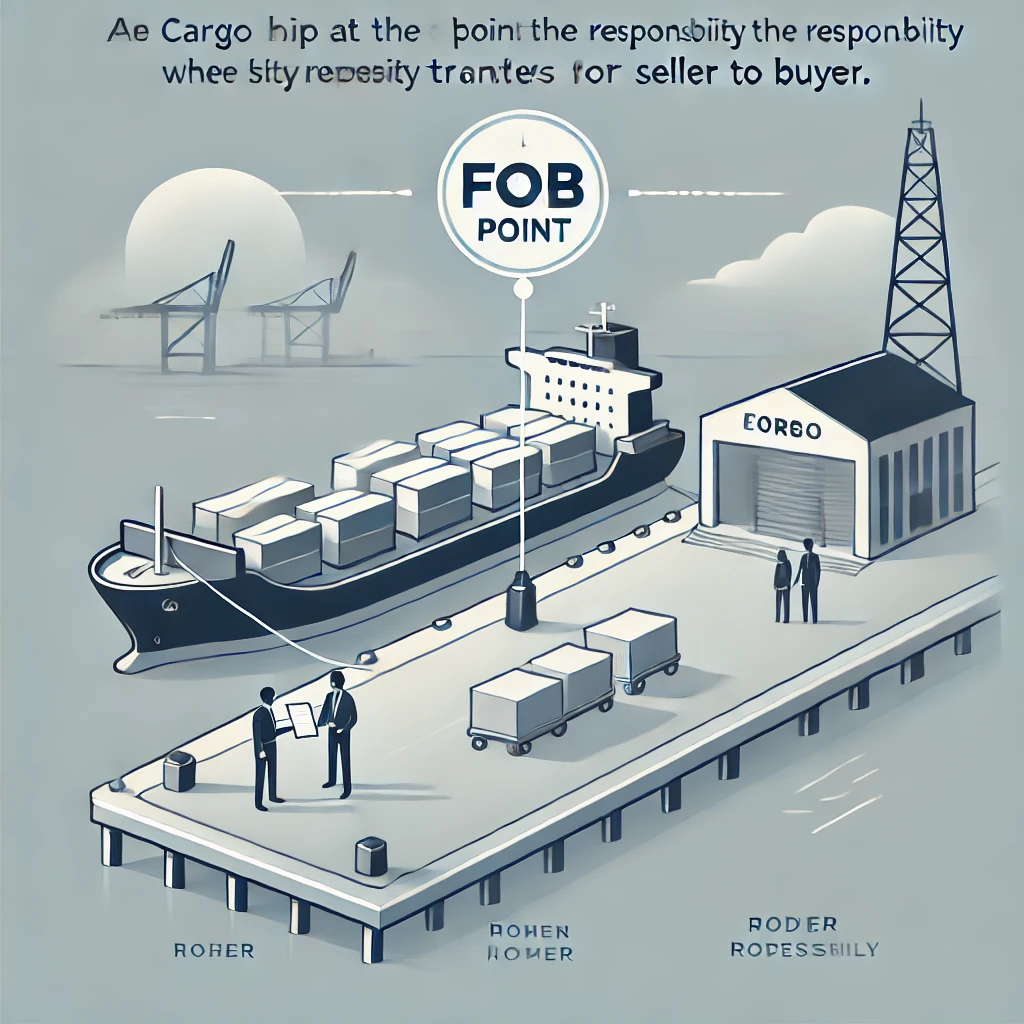
Freight on Board (FOB) is a shipping term defining when ownership and liability transfer from seller to buyer. It plays a crucial role in international trade by setting clear responsibilities for costs and risks during transit.
📊 Key Features of Freight on Board
- 📍 Point of Transfer: Determines the exact moment ownership shifts from seller to buyer.
- 💰 Cost Responsibility: Specifies who covers shipping, insurance, and loading expenses.
- ⚙️ Types of FOB Terms:
- 🏢 FOB Origin: Buyer assumes responsibility once the goods leave the seller’s premises.
- 🛳️ FOB Destination: Seller is liable until the shipment reaches the buyer.
🚀 Practical Uses of Freight on Board
- 🌎 International Trade: Provides clarity on financial and risk responsibilities.
- 📊 Purchase Orders and Contracts: Frequently appears in commercial agreements.
- 📦 Inventory Management: Affects when businesses record shipments in their inventory.
🔑 Importance of Freight on Board in Business
- 💰 Cost Management: Reduces disputes by outlining financial duties.
- 📜 Legal Protection: Establishes liability boundaries for losses or damages.
- ⚙️ Operational Efficiency: Simplifies logistics planning and coordination.
💡 Tips for Using Freight on Board Terms
- ✅ Use Clear Language: Specify FOB Origin or Destination in contracts.
- 🛡️ Insure High-Value Shipments: Protect against transit risks.
- 📞 Coordinate with Partners: Ensure shared understanding of shipping terms.
🌍 Comparing FOB with Other Incoterms
- FOB vs. CIF: CIF includes insurance, while FOB does not.
- FOB vs. EXW: EXW transfers responsibility earlier than FOB.
- FOB vs. DDP: DDP places full cost responsibility on the seller until delivery.
📚 Real-World Example
A supplier in China ships electronics to a U.S. retailer under FOB Shanghai terms. The retailer assumes risk once the shipment leaves the port, meaning any damage during ocean transit is their responsibility.
🚀 Advanced Insights: Modern Uses of FOB
- 📊 Digital Freight Management: Platforms automate FOB contract creation and tracking.
- 🌱 Sustainability Practices: FOB terms help businesses manage emissions and fuel costs.
- 💻 FOB in E-commerce: Crucial for drop shipping operations.
✅ Conclusion
Freight on Board (FOB) is a vital Incoterm that sets clear guidelines for cost and risk-sharing in global trade. Mastering its uses and variations helps businesses navigate international shipping efficiently while minimizing disputes and optimizing costs.
